The use of tomography and computed tomography (CT) provided practitioners with the ability to assess the quantity and quality of bone and critical anatomic structures before dental implant surgery.
The basic purposes for the use of CT are the following
(1) The determination of the quality and the quantity of bone
(2) Evaluation of pathologies
(3) Follow-up of regions where extensive surgery is performed
(4) The evaluation of potential recipient sites for implant placement, particularly with dental implant surgical guides
(5) Predictable implant placement with diagnostic/surgical templates/guides and advanced radiographic imaging
The advantages of CBCT guided implant placement
Accurate planning for dental implant placement, diameter and length
Accurately plan for necessary adjunctive treatment like bone grafting procedures
Decreased risks for nerve and arterial damage and generally less complications
Minimally invasive surgery
Shorter surgeries
Accuracy
Predictable restorative procedures
Decreases pain and discomfort in the immediate postoperative period
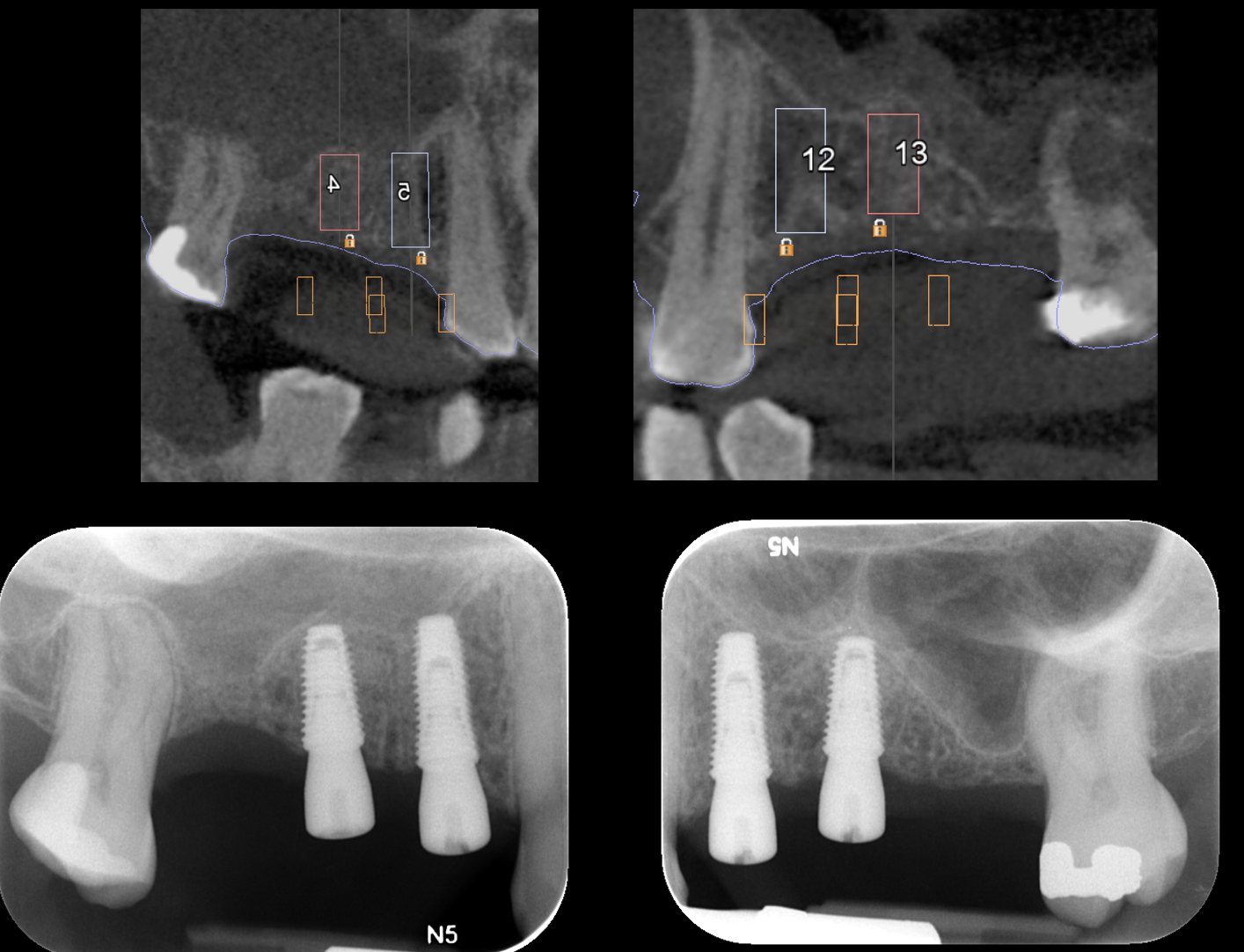
Example of a guided dental implant case
3D printed surgical guides
Plan and Execution, note the accuracy of the radiographs compared to the plan above